Return to flip book view
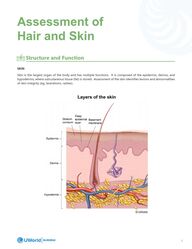
Message Assessment of Hair and Skin1Structure and FunctionSkinSkin is the largest organ of the body and has multiple functions. It is composed of the epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis, where subcutaneous tissue (fat) is stored. Assessment of the skin identifies lesions and abnormalities of skin integrity (eg, lacerations, rashes).
2Functions of the skin include: Protection y Protects from pathogens, microorganisms, and physical injury ○ Replaces damaged cells for wound repair if injury or trauma occursThermoregulation y Adapts to environment y Temperature regulation ○ Allows heat to dissipate via the sweat glands ○ Stores heat via subcutaneous tissue insulationFluid balance y Aids in maintaining the body's fluid balance by preventing the loss of water and electrolytes y Allows for waste excretion via sweatSensory perception y Detects touch, pain, and temperature changes through nerves and sensory receptors in the bodyVitamin D Synthesis y Ultraviolet (UV) light converts cholesterol into vitamin D on the surface of the skin.Identification y Gives clients unique qualities, including skin color and fingerprintsHairHair forms from threads of keratin. Sebum, an oil produced by sebaceous glands, is excreted via the hair follicles and is responsible for lubricating the skin and preventing water loss.
3Subjective AssessmentA subjective assessment of the hair and skin includes asking questions such as: ● "Are you wearing a wig or a hairpiece?" ● "Have you noticed any changes in hair growth or loss of hair?" ● "Are you currently receiving chemotherapy, or have you received chemotherapy in the past?" ○ Cancer treatment can significantly affect hair growth and the condition of the skin, leading to hair loss, skin dryness, redness, and pruritus. ● "Are you currently using topical or oral medication to facilitate hair growth?" ● "Have you experienced a decrease in appetite or nutrition?" ○ Malnutrition and lack of protein can alter hair growth and skin cell turnover. ● "Are you experiencing dry scalp or itchiness?" ● "Do you have any skin conditions?" ● "How much sun exposure do you receive each day?" ● "Do you use a tanning bed?" ● "Do you wear sunscreen when exposed to UV rays?"Objective Assessment: SkinAn objective assessment of the skin includes inspection (ie, visual investigation) and palpitation (ie, investigation via touch). Inspection begins as soon as the nurse and the client meet. Palpation should be gentle and slow, with tender areas assessed last. inSpection ● Skin pigmentation and consistency of pigmentation ○ Assess for the presence of cyanosis, jaundice, pallor, or redness. ● The presence of moles (nevi) ○ If the client has moles, the nurse should document the symmetry and pigmentation of the moles, as well as whether or not the mole has a smooth border. ● Bruising or lesions ● Mucous membranes ○ Color and moisture indicate hydration status.palpitation ● Warmth and consistency of skin temperature ○ The hands and feet may feel cooler. ● Skin texture ○ Smoothness, firmness, and thickness ● Presence of edema ○ Document where the edema is and whether it is pitting (eg, +1, +2).All assessment findings, normal or abnormal, should be documented. Abnormal findings must be reported to the health care provider (HCP).
4Objective Assessment: HairAn objective assessment of the hair includes inspection: ● Color and distribution of the hair ○ Assess whether color and pigment are evenly distributed. ● Hair texture ○ Assessment and documentation may include whether the hair is coarse or fine, shiny and smooth or dull, and straight or curly. ● Eyebrows and eyelashes ○ Clients with alopecia may not have eyebrows or eyelashes. Stress and aging can also affect hair growth of the eyebrows and eyelashes. The presence of both should be documented. ● Scalp ○ The scalp should be smooth and without lesions. AlterationsSkin alterations, or abnormal findings, should also be documented. Examples of skin alterations include: ● Pallor, cyanosis (ie, blue appearance to the skin related to lack of oxygen and perfusion) ● Erythema (ie, reddened skin) ○ Potential causes include fever, inflammation, and infection (eg, cellulitis). ● Jaundice (ie, yellowed skin) ○ Potential causes include increased bilirubin and liver cirrhosis. ● Lesions, lacerations, abrasions ● Skin cancer ○ Nevi ≥6 mm are at increased risk for dysplasia and cancer ○ ABCDE can be used to assess the risk for melanoma • Asymmetric, Borders (irregular), Color changes, Diameter, Elevation
5Hair alterationS ● Alopecia (ie, hair loss) ○ May be related to chemotherapy, hypothyroidism, genetics ● Hirsutism (ie, excessive hair growth) ● Seborrhea (ie, dandruff) ● Pediculus capitis (ie, head lice) ● Vitiligo (ie, well-demarcated, depigmented patches)Age-Related ConsiderationsPediatrics Older Adults y The skin of pediatric clients is not fully developed, which leads to an increased risk for fluid loss. y Although lanugo typically disappears prior to birth, it may be present in newborns, especially in premature infants. Lanugo is present in utero to help protect the fetus and provides warmth. y Coarse pubic and axillary hair begins to grow in adolescents. y Male clients begin to grow facial hair during puberty. y Older adults have decreased elasticity of the skin; the skin becomes more dry and thin. y Wrinkles develop over time, becoming more pronounced with age. y The skin pigmentation is increasingly uneven. y Changes in hair color occur, and the hair becomes thin and dull.
6Nursing InterventionsHealtH promotion ● The nurse should instruct clients to perform routine skin assessments. ○ Helpful for early detection of potential conditions such as melanoma ● Clients should be taught about appropriate sun protection: ○ Apply sunscreen when outdoors. ○ Minimize sun exposure between 10 AM and 4 PM. ○ Wear sun-protective clothing (eg, long-sleeved shirts, wide-brim hats) when outdoors. ○ Avoid the use of tanning beds and excessive exposure to UV light.Documentation ● The nurse must document all assessment findings. ● Abnormal findings should be reported to the HCP.
7Check for Understanding 1The nurse is teaching a client about the functions of the skin. Which of the following should the nurse include in the teaching? Select all that apply.a) "The skin provides protection from injury."b) "The skin produces vitamin E."c) "The skin helps regulate body temperature."d) "The skin maintains body fluid balance."e) "The skin provides a barrier against microorganisms."Check for Understanding 2The nurse is preparing to assess a client's skin for potential skin cancer using the acronym ABCDE. The nurse should recognize that this acronym stands fora) asymmetry, brown, circular, diameter, elevationb) abrasive, border, color changes, decrease in size, elevationc) asymmetry, border, color changes, diameter, elevationd) actual size, balding, circular, diameter, elevationCheck for Understanding 3The nurse is teaching a client about sun protection. Which of the following should the nurse include in the teaching? Select all that apply.a) "Perform routine skin assessments at home."b) "Avoid the use of tanning beds."c) "There is no need to wear sunscreen if it is cloudy outside."d) "Limit sun exposure between 10 AM and 4 PM."e) "Wear short-sleeved shirts when outdoors to prevent overheating.Answers1) a, c, d, e2) c3) a, b, d