Return to flip book view
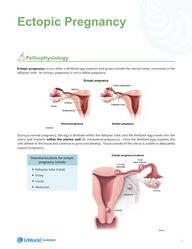
Message 1Ectopic PregnancyPathophysiology Ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants and grows outside the uterine cavity, commonly in the fallopian tube. An ectopic pregnancy is not a viable pregnancy. During a normal pregnancy, the egg is fertilized within the fallopian tube, and the fertilized egg travels into the uterus and implants within the uterine wall (ie, intrauterine pregnancy). Once the fertilized egg implants, the cells adhere to the tissue and continue to grow and develop. Tissue outside of the uterus is unable to adequately support pregnancy.Potential locations for ectopic pregnancy include: y Fallopian tube (tubal) y Ovary y Cervix y Abdomen
2Risk FactorsFactors that increase the risk for ectopic pregnancy include: ● Previous ectopic pregnancy ● Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) ○ inflammation of the fallopian tubes ○ it difficult for the fertilized egg to pass through the tube and reach the uterus ● Previous abdominal or pelvic surgical procedures ○ Can increase the risk for future ectopic pregnancies from scarring and adhesion formation of the fallopian tubes ● Intrauterine device (IUD) ○ pregnancy to implant outside of the uterus ● Smoking ○ Has been associated with an increased risk for an ectopic pregnancy ● Fertility treatments ○ ● Endometriosis ○ The presence of abnormal uterine tissue can cause scarring and adhesions ManifestationsManifestations of an ectopic pregnancy include typical symptoms of pregnancy, as well as additional symptoms specific to ectopic implantation.Typical pregnancy symptoms y No menstrual period y Positive pregnancy test ○ Because of the presence of the pregnancy hormone, hCG, that occurs when the egg is fertilized and begins to grow; however, hCG levels in an ectopic pregnancy may rise slower or be lower than expected for a normal intrauterine pregnancy
3Ectopic pregnancy symptoms y Unilateral lower abdominal pain ○ Sharp or stabbing pain that may vary in intensity but is usually persistent and worsens over time y Abnormal vaginal bleeding ○ May be continuous or intermittent y Visualization of the pregnancy outside of the uterus during ultrasonography performed by the health care providerComplicationsA ruptured ectopic pregnancy is a potentially life-threatening complication that occurs when the ectopic pregnancy continues to grow and eventually ruptures. Ruptured ectopic pregnancy requires immediate intervention (eg, surgery, blood product administration) because the rupture leads to internal bleeding.Manifestations of a ruptured ectopic pregnancy include:Severe, unilateral abdominal pain ● Abdominal pain on the side of the ectopic pregnancy intensifies rapidly as the tube rupturesHemodynamic inStability ● Hypotension from internal bleeding ● Tachycardia occurs because the body attempts to compensate for inadequate blood pressure to maintain adequate circulation ● Dizziness, light-headedness, and/or syncope can occur from hypotension and reduced blood flow to the brainreferred SHoulder pain ● and phrenic nerve due to intraabdominal bleeding is felt as shoulder pain A ruptured ectopic pregnancy is an obstetric surgical emergency and requires immediate intervention.
4InterventionsThe plan of care for a client who has an ectopic pregnancy includes:Pharmacological intervention y Methotrexate ○ Methotrexate is a folate antagonist used for nonsurgical treatment of an early, unruptured ectopic pregnancy ○ Methotrexate inhibits the growth of rapidly dividing embryonic cells by causing cellular folate depletion, leading to impaired DNA synthesis ○ Tubal rupture is still possible after methotrexate administration y Pain management ○ because opioid analgesics can suppress signs (eg, pain) of a ruptured ectopic pregnancy.Surgical intervention y Surgical removal of the ectopic pregnancy via laparotomy may be indicated when: ○ Methotrexate administration is ineffective ○ Ectopic pregnancy is detected at an advanced gestational stage, risking rupture due to size ○ There are signs of rupture, which may require removal of the fallopian tube, as well as the ectopic pregnancyBereavement care y chaplain services, to the client and the family and encourage them to join a support group.Client TeachingteacHing ● Manifestations of ruptured ectopic pregnancy ○ Educate the client about symptoms to monitor for and when to notify the health care provider ● Methotrexate teaching, if prescribed: ○ ○ Repeat hCG testing to monitor the effectiveness of methotrexate treatment because a stable or increasing hCG level may indicate that an additional dose is needed ○ Avoid becoming pregnant again until hCG is not detectable ● Monitoring for depression ○ Clients who experience early pregnancy loss may experience grief and are at risk for developing depression
5Check for Understanding 1The nurse is planning a staff education program about ectopic pregnancy. Which of the following information should the nurse include?a) "The fertilized egg implants outside of the uterine cavity."b) c) "There will not be any pregnancy signs or a positive pregnancy test."d) Check for Understanding 2The nurse is screening clients for those at risk for ectopic pregnancy. Which of the following factors would increase a client’s risk for ectopic pregnancy? Select all that apply.a) endometriosisb) c) daily alcohol consumptiond) history of pelvic inflammatory diseasee) achieving pregnancy via in vitro fertilizationCheck for Understanding 3The nurse is assessing a client with a suspected ruptured ectopic pregnancy. Which of the following findings would be consistent with a ruptured ectopic pregnancy? Select all that apply.a) hypertensionb) bilateral abdominal painc) light-headedness and syncoped) referred pain felt in the shouldere) uterine enlargement that is greater than gestational ageAnswersaa,d,ec,d